Introduction
MVP and prototype are two common terms used in the product development process. However, many people are unsure of the difference between the two. In this article, we will explore the concepts of MVP and prototype, highlight their differences, and discuss the factors to consider when choosing between the two.
What is an MVP?
A Minimum Viable Product (MVP) is a version of a product with just enough features to satisfy early customers and provide valuable feedback for future development. The main goal of an MVP is to test the viability of a product or idea in the market with minimal resources and effort.
This is a great example of how one can start to develop and launch a minimum viable product by implementing at first the most simple product with the most essential functionality that makes the early product already usable.
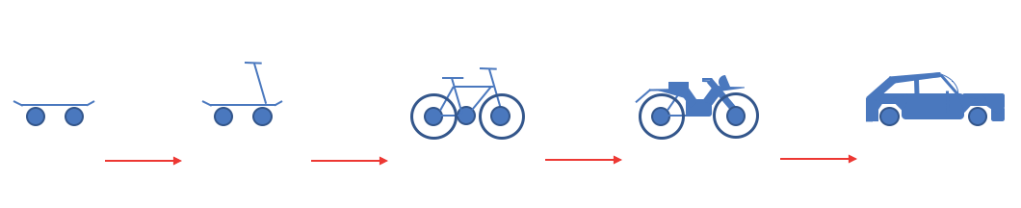
Illustration by Teemu – Own work, CC BY-SA 4.0
What is a prototype?
A prototype is a physical or digital representation of a product that is used to test and refine its design and functionality. Prototypes can be used to gather feedback from stakeholders, identify potential issues, and validate assumptions before investing in full-scale development.
Differences between MVP and prototype
The following table summarizes the key differences between MVP and prototype:
| Characteristic | MVP | Prototype |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Testing the viability of a product | Refining the design and functionality of a product |
| Stage of development | Developed after initial market research and validation of the idea | Created during the design phase |
| Functionality | Typically a functional product that can be used by early customers. Provides basic functionalities that solve a specific problem for users. | May not have all the functionalities and is mainly used for testing and gathering feedback. May contain only simulated functionalities for internal review and testing. |
| Cost | Generally more expensive due to its readiness for public usage. | Usually cheaper as it is intended for internal use. |
| Complexity | May involve a more complex development process. | Generally simpler to produce. |
When to choose an MVP
An MVP is a good choice when you:
- Have already conducted market research and validated your idea
- Need to test the viability of your product in the market
- Want to gather real-world feedback from early customers
- Have limited resources and time
When to choose a prototype
A prototype is a good choice when you:
- Are still in the early design phase
- Want to visualize and refine your product
- Need to gather feedback from stakeholders
- Want to test different design options
Factors to consider when choosing between MVP and prototype
When deciding between MVP and prototype, there are several factors to consider, including:
- Stage of product development: Consider the stage of your product development. If you have already conducted market research and validated your idea, an MVP might be the next logical step. If you are still in the early design phase, a prototype would be more suitable.
- Available resources and time: Developing an MVP requires more effort as it involves building a functional product that can be used by early customers. Prototyping, on the other hand, can be done using various tools and techniques, depending on the complexity of the product.
- Target audience and their preferences: If you have a clear understanding of your target audience and their needs, an MVP can help validate your assumptions and ensure that you are building something they actually want. If you are still exploring different design options and want to gather feedback from a wider range of stakeholders, a prototype can provide valuable insights.
Conclusion
MVP and prototype are both valuable tools in the product development process. The best choice for you will depend on your specific needs and goals. Consider the factors discussed in this article to make an informed decision.
