Lean startup is a business approach that aims to reduce waste, increase customer feedback, and experiment with minimal viable products (MVPs) to find a scalable and repeatable business model. It was popularized by Eric Ries and Steve Blank, who applied it to technology and internet startups, but it can be used in any industry or context.
Origin of Lean Startup
The lean startup method emerged from the observation that many startups fail not because they lack a good product, but because they lack a viable market. Traditional business planning methods, such as writing detailed business plans and launching fully-featured products, are often too slow and rigid for the uncertain and dynamic environment of startups. Ries and Blank proposed a new approach that focuses on learning from customers and testing assumptions as quickly and cheaply as possible, using MVPs as experiments. They drew inspiration from lean manufacturing principles, such as eliminating waste, optimizing value, and continuous improvement.
Benefits of Lean Startup
The lean startup method has several benefits for entrepreneurs and founders, such as:
- It helps them validate their ideas and assumptions before investing too much time and money into building products that nobody wants.
- It enables them to adapt to changing customer needs and preferences and pivot their strategy when necessary.
- It fosters a culture of innovation and experimentation, where failure is seen as an opportunity to learn and improve.
- It increases customer satisfaction and loyalty, by involving them in the product development process and delivering value faster.
Drawbacks of Lean Startup
The lean startup method is not without its challenges and limitations, such as:
- It requires a high level of discipline and rigor to design and execute valid experiments, measure the right metrics, and interpret the results objectively.
- It may lead to a loss of vision and creativity, by focusing too much on what customers want today, rather than anticipating what they will want tomorrow.
- It may neglect other important aspects of running a business, such as training, communication, HR policies, and partner relationships.
- It may not be suitable for every type of product or market, especially those that require high upfront costs, long development cycles, or complex regulations.
The Lean Startup Cycle and its components
The Lean Startup Cycle is a customer-centric approach and an iterative process that emphasizes validated learning and continuous improvement. The cycle consists of three main components. But even before you start the cycle, you need an idea!
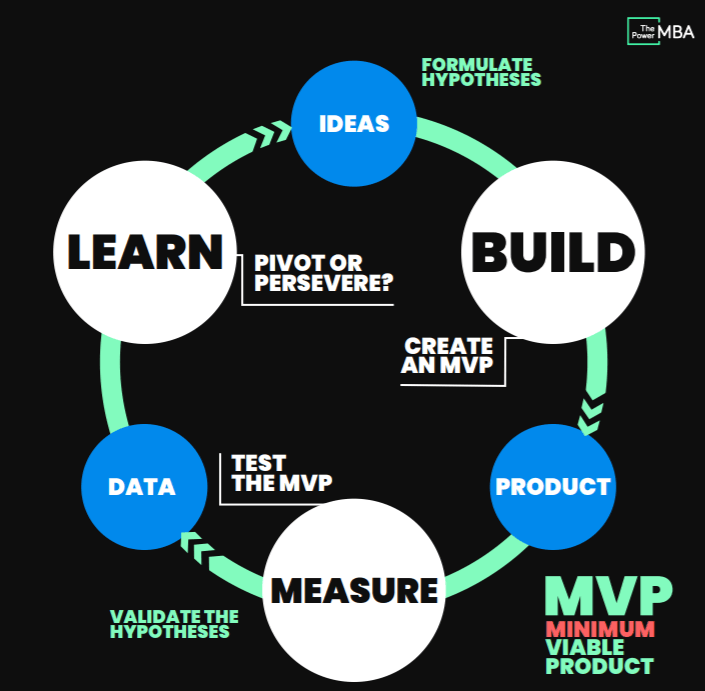
The illustration is from The Power MBA!
1. Build:
The first step is to build a minimum viable product (MVP). An MVP is a product with just enough features to be usable by early customers and allow for the collection of valuable feedback. The goal is to build an MVP quickly and efficiently, without wasting time and resources on features that customers may not want or need.
2. Measure:
Once the MVP is built, it is important to measure its performance against key metrics. These metrics can include customer engagement, usage patterns, and conversion rates. By measuring the performance of the MVP, entrepreneurs can gain valuable insights into what customers want and need.
3. Learn:
The final step is to learn from the data that has been collected. This data can be used to validate or invalidate the initial hypotheses about the product. If the data shows that the product is not meeting the needs of customers, then it is time to pivot or make significant changes to the product. If the data shows that the product is on the right track, then it is time to build on the success and continue to iterate and improve.
The Lean Startup Cycle is not a linear process. Instead, it is an iterative process that involves constantly going back and forth between building, measuring, and learning. This allows entrepreneurs to quickly identify what is working and what is not, and to make changes accordingly.
- Ideas: Generate and explore new ideas for products or services that address customer needs.
- Build: Create a minimum viable product (MVP) with just enough features to test the core assumptions and gather feedback.
- Measure: Collect data and metrics to evaluate the MVP’s performance and user behavior.
- Learn: Analyze the data to validate or invalidate assumptions, identify areas for improvement, and make informed decisions.
Use Cases of the Lean Startup Methodology
The Lean Startup methodology has been successfully applied across a wide range of industries and business types, including:
- Software Development: Startups and established companies alike use the Lean Startup approach to develop and launch new software products with minimal risk and increased customer satisfaction.
- Hardware Prototyping: Hardware startups leverage the Lean Startup methodology to create and iterate on prototypes quickly, gathering feedback from potential customers early on.
- Service Design: Service-based businesses can utilize the Lean Startup approach to test and refine service offerings based on customer feedback, ensuring a seamless and valuable experience.
- Business Model Innovation: Established companies can use the Lean Startup methodology to experiment with new business models and revenue streams, driving innovation without disrupting their core operations.
Here are some commercial examples:
- Dropbox: The file-sharing service used a simple video to demonstrate its MVP and test customer demand, before building the actual product.
- Zappos: The online shoe retailer started by buying shoes from local stores and selling them online, to test customer willingness to buy shoes online, before building its own inventory and distribution system.
- Airbnb: The home-sharing platform started by renting out air mattresses in the founders’ apartment, to test customer interest in alternative accommodation options, before expanding its offerings and features.
- Spotify: The music streaming service launched in beta mode with limited features and invites, to test customer feedback and retention, before rolling out its full product and subscription model.
Conclusion
The Lean Startup methodology has revolutionized the way entrepreneurs and businesses approach innovation and product development. By emphasizing rapid experimentation, validated learning, and iterative product refinement, the Lean Startup approach has helped countless startups achieve success and has even been adopted by established companies seeking to foster agility and innovation. While the Lean Startup methodology is not without its drawbacks, its benefits far outweigh its limitations, making it a powerful tool for navigating the ever-changing landscape of business.
